Introduction to Course Satisfaction Questionnaires.
Significance of Evaluating Satisfaction with the Course.
The course satisfaction is obligatory to determine what students think about the learning process. It assists the teaching institutions in finding out the strengths and weaknesses in their teaching method, course content, and delivery as a whole.
Through gathering student feedback, administrators will be able to make informed choices to enhance the course design, get more engagement, and improve overall academic performance. The course satisfaction surveys are also used in long-term enhancement of curriculum planning and development of the faculty.
The most important elements of a Questionnaire on course satisfaction.
A perfectly organized questionnaire of course satisfaction usually contains several blocks, i.e., course material, instructor performance, learning aids, and experience. Both parts include questions that seek to summarize the students’ views regarding various issues of the course.
Questions are normally put in Likert scale format, where the respondent is expected to respond to levels in which they agree or are satisfied. Other open-ended questions will give qualitative data, which will supplement quantitative data and give greater insight.
Understanding the concept of analyzing the data
Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) is a statistical method that is applied to reveal the latent structure of a group of variables. When used in the context of a course satisfaction questionnaire, EFA aids in defining groups of similar items, also referred to as factors, that depict certain dimensions of student satisfaction.
This approach enables researchers to simplify complex data, identify patterns, and to make sure that items posed in the survey are appropriate in that they measure the constructs that they are designed to measure.
Distinctions Among EFA and Confirmatory Factor Analysis.
Whereas EFA learns and examines the data in order to determine possible factors, without any prior expectations, Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) tests a previously defined factor structure.
EFA works best at the preliminary phases of questionnaire design since it helps the researcher to explore meaningful constructs. CFA, however, is employed as a follow-up to EFA in order to make sure that the factors measured in a study are in concurrence with theoretical predictions, which in turn, gives more evidence of validity.
Course Satisfaction Questionnaire Design

Establishing Relevant Constructs.
The initial process of questionnaire design is to establish the appropriate constructs/dimensions of course satisfaction. These can be the quality of the teaching, the content of a course, the interaction between students, the way the course is assessed, and the learning environment.
Researchers are able to use literature review, faculty members, and institutional goals to decide on the major constructs to capture in the survey.
Composing Good Questionnaire Items.
The question items must be clear, concise,e and not biased. The questions should only deal with one idea at a time to prevent confusion. The language employed is very simple, such that students of both backgrounds can comprehend the question and give the correct responses.
Moreover, a combination of questions with positive and negative wording would decrease the bias in the responses and enhance the quality of the received data.
Course Satisfaction Methods of Data Collection.
Online Surveys versus Paper-Based Questionnaires.
There are merits as well as demerits of both online and paper-based surveys. An online survey is convenient, cost-efficient, and can be used to collect data faster.
Questionnaires that are paper-based can prove more appropriate in environments where the internet is not widely available or in smaller classes. The decision on the right technique is based on the audience to be targeted, the resources at hand, and the response rate.
Assuring Reliable and Valid Responses.
In order to get the right data, one must have anonymity and confidentiality. Honest answers can be encouraged bythe use of clear instructions, simple questions, and a reasonable length of the survey.
It may be possible to pilot test the questionnaire, identify confusing questions, and make sure the survey measures the intended constructs.
Ready Ware Data Preparation: Data preparation before Exploratory Factor Analysis.
Data Cleaning and Screening. Before performing EFA, the researchers have to clean the data; they have to check missing values, outliers, and unreliable responses.
The accuracy of the factor analysis is achieved by deleting incomplete or unreliable data. Descriptive statistics screening and all items having adequate variability are also part of screening the data.
Evaluation of Sampling Adequacy.
Factor analysis is dependent on the adequacy of sampling. The most common measures used by the researchers to decide whether the data are appropriate to use EFA are the Kaiser Meyer Olkin (KMO) and Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity.
The greater the value of KMO, the greater the correlations between items and therefore, the more reliable the factor is obtained.
Completing Exploratory Factor Analysis.
Extraction Methods in EFA
The most popular extraction techniques are Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Principal Axis Factoring (PAF). PCA helps in simplifying the data by dimensional reduction, and PAF is aimed at determining latent constructs. The extraction method used will be determined by the aims of the research and the type of data to be extracted.
The determination of the Number of Factors.
The choice of the number of factors to be retained is important. Eigenvalues that are above one, scree plots, and parallel analysis are some of the techniques that will assist in establishing the best number of factors. Having too many or too few factors will give a false impression of the underlying structure and decrease the usefulness of the survey.
Factor Rotation Techniques
Factor rotation eases the interpretation process by making loadings clearer. The common are varimax (orthogonal) and oblique (oblimin) rotations.
Although varimax does not assume any correlation between factors, oblimin does not rule out correlations, and these correlations may be more useful in the measurement of course satisfaction dimensions.
Interpreting EFA Results
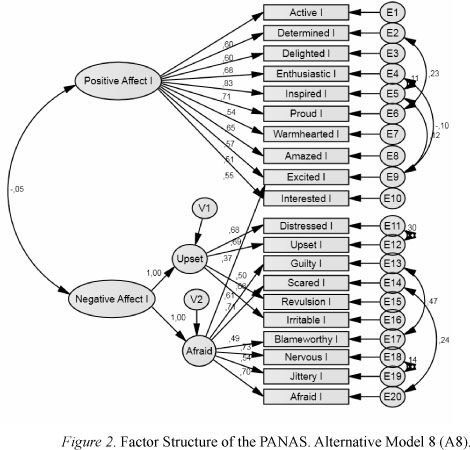
Factor loadings show how strong the relationship is between the items in the survey and the underlying factors. Large loadings indicate that an item is a strong indicator of a factor, whereas low loadings may indicate revision or elimination.
The analysis of factor loadings can assist the researcher in determining the best questions that capture each construct.
Naming and Defining Factors
After the identification of factors, they should be named and defined depending on the items they contain.
An example can be the factor that includes the items of teaching clarity and instructor engagement, being called T-Teaching Effectiveness. Proper naming will bring clarity and help the stakeholders interpret the survey results.
Questionnaire validation with the help of EFA.
Reliability Analysis of Factors.
The internal consistency of factors is measured by reliability analysis, which is usually done using Cronbach’s alpha.
The alpha value is high, and this means the items in a factor have always measured the same construct. Lowlyreliabley factors might require revision of items or the inclusion of new questions.
Revising the questionnaire based on findings.
Results of EFA help the researchers to revise the questionnaire. Items that would not load well on any factor can be dropped, and new items can be included to reinforce weak constructs.
The ongoing improvement process will ensure that the questionnaire offers useful and valid information that can be used to evaluate the courses.
Applications of Course Satisfaction Questionnaires.

Enhancing Teaching Methods
The course satisfaction survey assists the instructors in knowing the effectiveness and the learning preferences of the students.
Through the analysis of the feedback, the instructors will be able to change their teaching strategies, add new teaching techniques to their instruction, and offer a more significant level of support to the learners when necessary to improve the learning outcomes.
Enhancing Student Learning Process.
Knowledge of satisfaction rates of students will enable the institutions to enhance the general learning process.
Changes in course format, study materials, and face-to-face communication in response to survey data may result in higher levels of engagement, motivation, and academic achievement.
Problems and Disadvantages of EFA in Questionnaire Design.
Potential Traps in Factor Analysis.
Small sample sizes, poorly constructed items, and failure to understand factor loadings can influence EFA. To prevent misleading results, the researchers need to provide sufficient data quality and select extraction and rotation techniques properly.
Weaknesses of Self-Reported Data.
The self-reported surveys are subject to either social desirability bias or false recollection. Although EFA enhances the construct validity, scholars are advised to combine the findings with other data, including performance measures and qualitative feedback.
Future Course Satisfaction Research.
Possible Surveys: Integrating Technology.
Learning management systems and digital tools allow the collection of feedback in real-time. Interactive dashboards, mobile-friendly surveys, and gamified questionnaires enhance the response rates and offer some dynamic insights into student satisfaction.
Application of Advanced Statistical Techniques.
Other sophisticated methods, such as Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) and machine learning, can reveal multi-faceted relationships between course factors and course learning outcomes. The techniques permit a deeper level of analysis, prediction, and interventions that are more individual in education.
FAQs
Why do we need to use a course satisfaction questionnaire?
It assists in gauging the perception of the students toward the quality of the courses and areas that can be improved.
Why should Exploratory Factor Analysis be applied in questionnaire design?
EFA finds unobservable factors and simplifies data to complex data, and makes sure surveys are a good match to constructs.
What is the difference between an online survey and a paper-based survey?
The online surveys are quicker and less expensive, whereas the paper surveys can be applied to regions with scarce internet connections.
What are the factor loadings of EFA?
Factor loadings indicate the extent to which a particular item is related to a particular factor or construct.
Does EFA enhance the process of teaching and learning?
Yes, through identifying areas of key satisfaction, teachers would be able to modify teaching procedures and improve learning among students.