Introduction to Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA)
What Makes CFA Different from EFA
CFA tests theories by determining whether the data are consistent with a predetermined structure, whereas EFA examines trends without predetermined assumptions.
CFA is applied by researchers when they are confident about the factors that should be measured and require strong statistical support for their models.
Significance of CFA in Contemporary Research
CFA assists the researcher in establishing correlations among variables, which will provide proper measurement.
It enhances theoretical constructs, scale quality, and valid decision-making in investigations across the fields of psychology, education, marketing, and the social sciences.
Major Concepts and Terms CFA
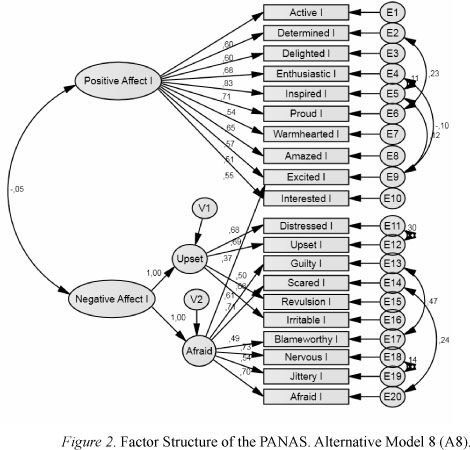
Observed Indicators and Latent Variables
Latent variables are unmeasurable hidden characteristics, and indicators are observable items that are used to measure them.
CFA links these items so as to enable researchers to know the degree to which the indicators represent the underlying concepts.
Explained Models of Measurement.
A measurement model indicates the relationship between the indicators and the latent variables.
CFA validates this structure and provides indicators to measure the desired concepts. Quality model facilitates reliability, theory testing, and sound research results.
Factor Loadings and Error Terms
Factor loadings indicate the intensity of the relationship between each indicator and its latent variable, and error terms indicate inaccuracy in measurement.
A larger loading and reduced error levels are positive signs of a better and more accurate measurement model in CFA.
Instructions for doing the Confirmatory Factor Analysis

Preparation and Cleaning of the Dataset.
Before the CFA is run, researchers begin by verifying missing values, outliers, and data normality.
Cleaning will guarantee proper results since the misfit of the model due to unprepared data can corrupt factor loadings or estimates of reliability, which will influence the analysis in general.
Construction of the Hypothesized Model.
The second stage will involve constructing a clear model to be developed on theory, determining latent variables, indicators, and anticipated relationships.
CFA is guided by this model, which assists the researchers in testing whether their hypotheses fit the real data setup.
Statistical Software CFA Running
The software typically used to perform CFA is AMOS, LISREL, MPLUS, or R-Lavaan.
These programs give estimates of the loadings of factors, the fit index, and error terms so that the researcher can compare the goodness of their proposed model to the actual patterns of datasets.
Model Fit Indices in CFA
Absolute Fit Indices (RMSEA, SRMR)
Absolute fit indices are used to determine the similarity between the model and the observed data.
A value of RMSEA and SRMR that is less than the recommended limit will regood fit and thus will allow researchers to make a judgment on whether their measurement model is realistic in terms of variable relationships.
Incremental Fit Indices (CFI, TLI)
Incremental indices, such as CFI and TLI, are used to compare the proposed model and a model of the baseline.
The values are higher, which are indicators of improvement and strong theoretical support, and research. Archers can use this to guide them in evaluating and refining their CFA results.
Parsimony Fit Indices
Parsimony indices measure model simplicity and are also accurate. They assist in making sure that researchers do not make the model too complicated.
A good, balanced model fits well without unwarranted complexity and promotes both practical and theoretical clarity.
Testing Reliability and Validity

Construct Reliability (CR)
Construct Reliability estimates internal consistency, which demonstrates whether indicators are always a measure of their latent variable.
The larger CR values are a sign of stable measures that enable researchers to have confidence in their scales and make it easier to confirm their conclusions in CFA studies.
Convergent and Discriminant Validity
Convergent validity establishes that indicators measure the same thing, whereas discriminant validity makes surensuresferent concepts are different.
The two help in the proper interpretation of the model, which minimises duplication and enhances the clarity of theoretical constructs.
Extracted Variance of the Means (AVE)
AVE is used to determine the extent to which the indicators explain their latent variable.
The high value of AVE indicates a high level of convergent validity, which assists researchers to establin establishing their measurement model, measuring significant shared variance between items.
All CFA CFAs face challenges, flaws, and solutions
Handling Poor Model Fit
Poor model fit may arise when the structure proposed by the hypothesis is not able to fit the data.
Researchers enhance fit through rechecking of loadings, manipulating of items, or reconsideration of theory so that the end model is a good representation of actual observations.
The Management of Modification Indices
Modification indices provide potential improvement in the model. They are applied carefully by researchers who should make sure that any changes are theoretically justified.
Correct interpretation prevents overfitting and maintains the measurement model in line witthe h the initial objectives of the research. the
Multicollinearity, Sample Size Problems
CFA results can be weakened by high indicator-indicator correlations and by small samples.
This is addressed by researchers by making certain that sample sizes are large enough anlarge d that there are items that do not overlap so that the model estimates can be constant and reliable.
Real Life Uses of CFA in Research
Baccalaureate in Psychology and Social Sciences
CFA is used to confirm the scales of such traits as stress, motivation, or personality in psychologists.
CFA is also used by social science researchers to validate theories and obtain proper measurements of intricate human behaviors and attitudes.
CFA Education and Behavioral Studies
Educational researchers use CFA to test the scales of student performance, tools of teaching efficiency, and behavior measurement models.
It makes sure that tests are based on actual learning achievement and not randomness or error of measurement.
Marketing and Organization Research CFA.
Marketing scholars apply CFA to affirm the customer satisfaction scale, brand loyloyaltye alty model, and cons,umer perception scale.
CFA is also used by organizations to examine leadership, attitudes of the employees, and the culture of the workplace.
Conclusion
Why CFA Enriches the Quality of the Research.
CFA enhances the quality of research by ensuring the right measurement, theoretical models, and bias reduction.
It guarantees sound scales, more robust conclusions, and more in-depth cognitiorelationshipsonhi,, ps and is indispensable to good academic studies.
FAQs
1. What do you think is the primary purpose of CFA?
CFA compares data to a theoretical model that has been established to affirm that the data has a relationship with the latent variables and indicators.
2. How is CFA different from EFA?
The EFA examines patterns in an unassuming manner, whereas the CFA analyzes a particular, theory-based structure.
3. What is the recommended size of the sample of CFA?
At least 200 individuals are often recommended to achieve stable, reliable model estimation.
4. What software is most appropriate for CFA?
The most common applications are AMOS, LISREL, Mplus, and R-Lavaan, which have good CFA results.
5. What is the importance of fit indices?
Fit indices are used to ascertain the fit of the hypothesized model and the observed data.